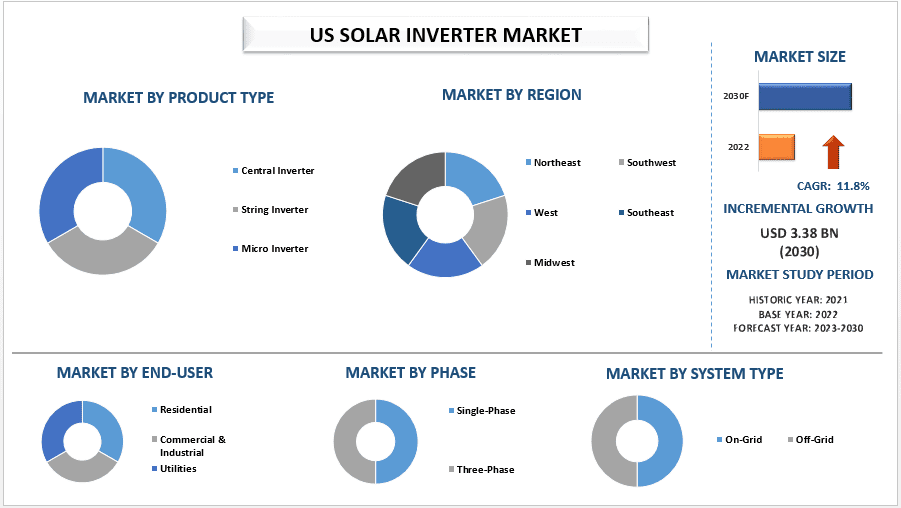
According to the UnivDatos, the rising sales of solar panels will drive the global scenario of the US Solar Inverter market and as per their “US Solar Inverter Market” report, the global market was valued at USD 1.37 billion in 2022, growing at a CAGR of 11.8% during the forecast period from 2023 – 2030 to reach USD 3.38 billion by 2030.
A solar inverter, also known as a photovoltaic (PV) inverter, is an important part of a solar energy system. Its main function is to convert the variable direct current (DC) output of photovoltaic panels to grid-frequency alternating current (AC), which can be fed into the commercial power grid or used in local off-grid power networks. This change allows the use of traditional AC-powered devices. Solar inverters are designed to absorb the fluctuating DC output of your panels and convert that power into 120 or 240-volt AC output. These replace the DC power collected by solar panels.
Access sample report (including graphs, charts, and figures): https://univdatos.com/reports/us-solar-inverter-market?popup=report-enquiry
Types of Solar Inverters
Solar inverters are classified into different types based on their functionality and the type of solar power system used. The main types are:
Ø String Inverter: String inverters are used in photovoltaic systems to convert direct current to alternating current. These are currently the most commonly used inverters and account for the majority of the inverter market worldwide. If one panel produces less power than the other panels due to certain reasons, such as shading, the other panels will start producing the same level of power as the affected panel.
Ø Power Optimizer: Power optimizers offer the same benefits as microinverters. Reduces the effects of shading. Using a power optimizer in your system is more cost-effective than using a microinverter.
Ø Microinverters: Microinverters and power optimization systems are more expensive than string inverters.
Furthermore, solar inverters can be classified into three types according to the grid connection: grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid inverters.
Ø On-grid solar inverter: Compatible with on-grid solar systems. H. Anything connected to the power grid. It plays an important role in converting direct current to alternating current.
Ø Off-grid solar inverter: An important part of an off-grid solar power system that converts DC power to AC power.
Ø Hybrid solar inverter: Works with both on-grid and off-grid solar power systems. These inverters are available in different input capacity ranges such as 12 Volt DC, 48 Volt DC, and even 96 Volt DC.
Government Policies Supporting the Solar Energy Industry
There has been a rise in demand for renewable energy and the United states of America is planning to diversify its energy portfolio in order to become less dependent on conventional sources of energy. The government has started addressing climate issues and have introduced many new renewable energy schemes to reduce carbon emissions. Governments across the world are coming together for initiatives such as Paris Climate Agreement and this is acting as a catalyst in the growth of the US Solar Inverter Market.
Along with national schemes, there are various types of policy that are driving Solar PV capacity growth, including auctions, feed-in tariffs, net-metering and contracts for difference.
The U.S. solar industry is subject to a variety of federal, state, and local guidelines and regulations. The federal government offers tax credits for investing in solar power, and many states have goals and policies to encourage the adoption of solar power. Important solar policies include the Build Back Better Act, Net Metering 3.0, and Section 201 tariffs.
The state’s solar carve-out program is also important. Many states are promoting solar energy development by requiring utilities to purchase SRECs produced by domestic solar PV systems as part of their obligations under the Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS). has created a solar renewable energy certificate (SREC) market. The Department of Energy wants to reduce the cost of solar energy by 60 percent by 2030 by investing in technology beyond crystalline silicon. The industry also faces rapidly evolving new requirements and challenges from various federal regulatory agencies.
Private companies are driving the growth of the Global US Solar Inverter Market
The private sector’s main activity in solar energy deployment can be divided into two categories:
Ø Companies investing in distributed (including rooftop) solar PV installations on their own buildings and premises – are responsible for almost 30% of total installed PV capacity as of 2021.
Ø Companies entering into corporate power purchase agreements (PPAs) – signing direct contracts with solar PV plant operators for the purchase of generated electricity. Solar PV plants dominate renewables PPAs, with a share of almost 75% in 2020.
U.S. businesses and top global brands are making historic investments in solar energy. As of June 2022, Meta leads the nation with the most solar capacity installed, followed closely by Amazon, Apple, Walmart and Microsoft. Nearly 19 gigawatts (GW) of solar capacity has been installed with commercial and corporate off-takers, more than half of which has come online since 2020.
Click here to view the Report Description & TOC: https://univdatos.com/reports/us-solar-inverter-market
Fortune 500 Companies Driving the Growth in Private Sector
SEIA’s annual Solar Means Business report shows that major U.S. corporations such as Meta, Amazon, Apple, Walmart, and Microsoft are investing in solar energy at an increasingly rapid rate. As of June 2022, the top corporate solar users in America have installed almost 19 GW of capacity across nearly 50,000 different facilities nationwide. Off-site solar made up much of the growth in corporate solar, with 77% of capacity since 2020 being off-site. Nearly 19 gigawatts (GW) of solar capacity has been installed with commercial and corporate off-takers, more than half of which has come online since 2020.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the US Solar Inverter market is poised for significant growth. The increasing demand for sustainable energy sources and the declining costs of solar energy systems are key factors driving this growth. Even in individual states such as Massachusetts, the solar energy market is shaped by net metering and a renewable portfolio standard with a solar goal, along with an accompanying SREC market. The Solar Massachusetts Renewable Target (SMART) program was established in 2018 and has driven significant solar deployment in the state, acting as a template for other states to follow.
Moreover, governments worldwide are promoting the adoption of solar energy systems to reduce carbon emissions. The U.S., for instance, has been investing in research for more efficient solar technology to make it more accessible for residential and commercial uses. Furthermore, advancements in battery technologies for solar energy storage are expected to boost the demand for solar inverters. Companies are also investing in better solar inverter systems, with several top-notch options available in the market. Therefore, the US Solar Inverter market is not only contributing to the growth of renewable energy but is also a promising sector for investment and development.
Contact Us:
UnivDatos
Contact Number – +1 978 733 0253
Email – contact@univdatos.com
Website – www.univdatos.com
Linkedin- https://www.linkedin.com/company/univ-datos-market-insight/mycompany/