
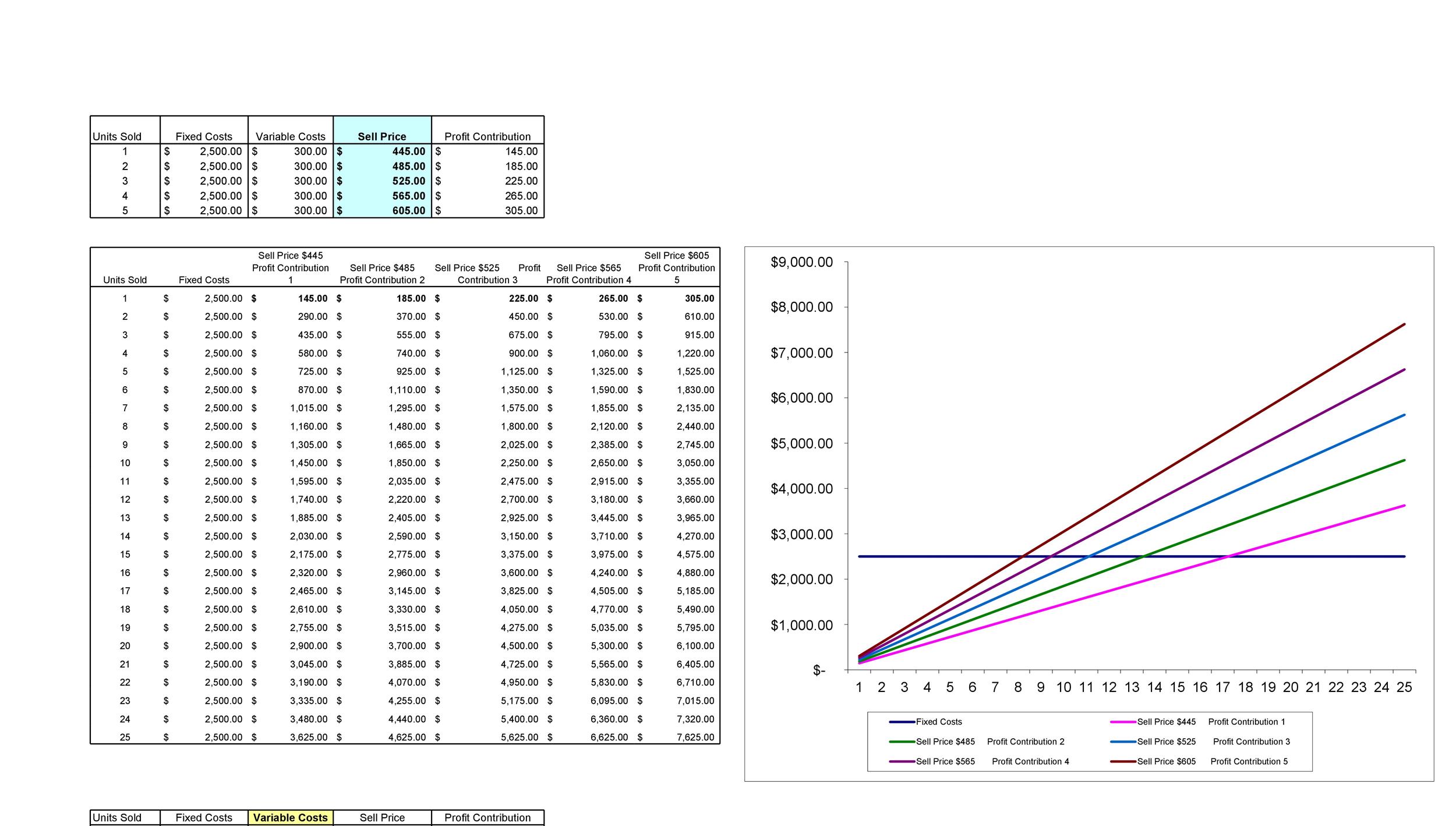
This will give visibility into the number of units to sell, or the sales revenue they need, to cover their variable and fixed costs. On the vertical axis, the breakeven chart plots the revenue, variable cost, and the fixed costs of the company, and on the horizontal axis, the volume is being plotted. The chart helps in portraying the company’s ability to earn a profit with the present cost structure. Break-even analysis helps businesses choose pricing strategies, and manage costs and operations. In stock and options trading, break-even analysis helps determine the minimum price movements required to cover trading costs and make a profit.
- The breakeven formula for a business provides a dollar figure that is needed to break even.
- Rent, insurance, utility bills and repairs are also considered fixed costs, since variations are minute and the amount does not directly depend on the number of items produced.
- Whatever option you choose, the important thing is that you are aware of these metrics and actively using them.
- Put another way; the break-even point is when the total revenues of a certain production level equal the total expenses of producing that product.
- Let’s assume she must incur a fixed cost of $45,000 to produce and sell a dress.
What Is the Breakeven Point (BEP)?
Break-even analysis also can be used to assess how sales volume would need to change to justify other potential investments. For instance, consider the possibility of keeping the price at $150, but having a celebrity endorse the dress (think Madonna!) for a fee of $20,000. Fixed costs are those that do not change no matter how many units are sold.
What is your current financial priority?
For Example, Labor rates will increase due to overtime if more units are produced. The break-even analysis also assumes that all units produced are also sold, which is not always the case. This tool fails to take into account the demand-side situation, since not all units produced are sold at the assumed price. In other words, if this dressmaker sells 1,125 units of this particular dress, then she will fully recover the $45,000 in fixed costs she invested in production and selling.
Move, manage, and grow your money
Let’s say you are thinking about changing your business model; for example, switching from buying inventory to doing drop shipping or vice-versa, you should do a break-even analysis. Your costs might vary significantly, and this will help you figure out if your prices need to change too. In other words, if the endorsement led to incremental sales of 525 dress units, the endorsement would break-even. If it led to incremental sales of greater than 525 dresses, it would increase profits. One way to calculate the break-even point is to determine the number of units to be produced for transitioning from loss to profit.
The relationship between contribution margin and breakeven point is that even a dollar of contribution margin chips away at a company’s fixed cost. A higher contribution reduces the number of units needed to break even because each unit contributes more towards covering fixed costs. Conversely, a lower contribution margin increases the breakeven point, requiring more units to be sold to cover fixed costs.
The following example of the break-even chart provides an outline of the most common type of break-even chart present. Each of the examples of the breakeven chart states the topic, relevant reasons, and additional comments wherever required. Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader.
Generally, to calculate the breakeven point in business, fixed costs are divided by the gross profit margin. When it comes to stocks, for example, if a trader bought a stock at $200, and nine months later, it reached $200 again after falling from $250, it would have reached the breakeven point. While the breakeven point is a valuable tool for decision-making, it has several limitations.
For example, if a product sells for $10 but only incurs $3 of variable costs per unit, the product has a contribution margin of $7. Note that a product’s contribution margin may change (i.e. it may become more or less efficient to manufacture additional goods). Break-even analysis is a tool for evaluating the profit potential of a business model and for evaluating various pricing strategies. You can easily compile fixed costs, variable costs, and pricing options in Excel to determine the break even point for your product. This is the number of units that you need to sell at the price you set in order to break even.
Total revenue can be calculated by multiplying the price at which goods or services are sold by number units sold. The contribution margin is determined public accounting ms by subtracting the variable costs from the price of a product. Every business must develop a break-even point calculation for their company.
Contribution margin, when expressed as percentage of sales is called contribution margin ratio. For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing. With the Fixed Costs at $66,000 we see, it would only be worthwhile if the dressmaker believed that the endorsement would result in total sales of 1,650 units. These costs are fixed as they do not change per the number of dresses sold. To show how break-even works, let’s take the hypothetical example of a high-end dressmaker. Let’s assume she must incur a fixed cost of $45,000 to produce and sell a dress.


