Introduction
The human brain is a complex network of cells that communicate through chemical signals. These chemical messengers, known as neurotransmitters, play a crucial role in regulating mood, cognition, and bodily functions. But how do neurotransmitters work, and what happens when they become imbalanced? This article explores the role of neurotransmitters, their functions, and their impact on mental health.
What Are Neurotransmitters?
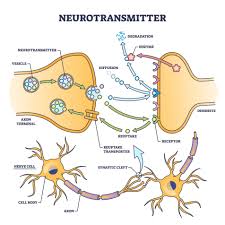
Neurotransmitters are chemical substances that transmit signals from one neuron to another across synapses. They are essential for brain function and influence various aspects of human behavior, including emotions, thought processes, and physical movements.
How Neurotransmitters Work
Neurons communicate using electrical and chemical signals. When a neuron is activated, it releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic gap. These chemicals bind to receptors on the next neuron, triggering a response. Once the signal is transmitted, Neurotransmitters are either broken down by enzymes or reabsorbed through a process called reuptake.
Types of Neurotransmitters and Their Functions
Neurotransmitters are classified into different categories based on their effects and functions. Here are some of the most important ones:
1. Excitatory Neurotransmitters
These neurotransmitters stimulate the brain and encourage the transmission of signals.
- Glutamate: The most abundant neurotransmitter in the brain, responsible for learning and memory.
- Acetylcholine: Involved in muscle activation, attention, and memory.
2. Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
These neurotransmitters reduce neural activity and help balance brain function.
- GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid): Helps calm the nervous system, reducing stress and anxiety.
- Glycine: Plays a role in motor control and processing sensory information.
3. Modulatory Neurotransmitters
These neurotransmitters influence multiple neurons and regulate broader brain functions.
- Dopamine: Associated with motivation, pleasure, and reward.
- Serotonin: Regulates mood, appetite, and sleep.
- Norepinephrine: Involved in alertness, arousal, and stress response.
- Endorphins: Natural painkillers that enhance pleasure and reduce stress.
The Role of Neurotransmitters in Mental Health
Neurotransmitters play a critical role in mental well-being. When their balance is disrupted, various psychological conditions can arise.
1. Depression
Low levels of serotonin and dopamine are linked to depression. Antidepressants such as SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors) help increase serotonin levels in the brain.
2. Anxiety Disorders
GABA deficiency is associated with heightened anxiety. Medications like benzodiazepines enhance GABA activity to promote relaxation.
3. Schizophrenia
An imbalance of dopamine is thought to contribute to schizophrenia. Antipsychotic medications target dopamine receptors to regulate its effects.
4. ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder)
Dopamine and norepinephrine imbalances can affect focus and impulse control. Stimulant medications help restore neurotransmitter balance.
Natural Ways to Support Neurotransmitter Health
Maintaining a healthy balance of neurotransmitters is essential for overall well-being. Here are some natural ways to support brain chemistry:
1. Proper Nutrition
Eating a balanced diet rich in amino acids, vitamins, and minerals supports neurotransmitter production.
- Tryptophan (found in turkey, eggs, and nuts) boosts serotonin levels.
- Tyrosine (found in dairy, soy, and bananas) supports dopamine production.
2. Regular Exercise
Physical activity increases dopamine, serotonin, and endorphin levels, enhancing mood and reducing stress.
3. Adequate Sleep
Sleep is crucial for neurotransmitter regulation. Poor sleep can lead to serotonin and dopamine imbalances.
4. Stress Management
Chronic stress depletes neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine. Mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help maintain balance.
5. Supplements and Herbs
Certain supplements and herbs support neurotransmitter function.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Enhance brain health and neurotransmitter efficiency.
- Magnesium: Helps regulate GABA levels.
- St. John’s Wort: May boost serotonin levels (consult a doctor before use).
Conclusion
Neurotransmitters are vital to mental health and overall well-being. Understanding their functions and maintaining a balanced lifestyle can support brain health and emotional stability. Whether through nutrition, exercise, sleep, or stress management, taking proactive steps can improve neurotransmitter function and enhance mental health.