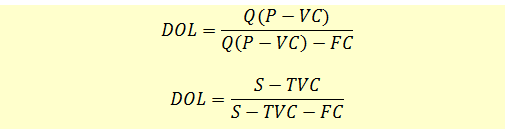
Where earnings are either equal to fixed financial charge or unfavorable, debt financing should not be encouraged. Based on calculations like those shown above, the finance manager can make appropriate decisions by comparing the cost of debt financing to the average return on investment. When calculating financial leverage, you should note that EBIT is a dependent variable that is determined by the level of EPS. The degree of combined leverage gives any business the optimal level of DOL and DOF. By now, we have understood the concept of Dol, its calculation, and examples. Let’s see how the measure can impact the company’s business and financial health.
Operating Leverage Formula
Specifically, DOL is the percentage change in income (usually taken as earnings before interest and tax, or EBIT) divided by the percentage change in the level of sales output. The Operating Leverage measures the proportion of a company’s cost structure that consists of fixed costs rather than variable costs. The impact of the high fixed costs is directly seen in the firm’s ability to manage revenue fluctuations. The high operating leverage reflects the inflexibility in managing costs and revenues. The DOL of a firm gives an instant look into the cost structure of the firm. The degree of operating leverage directly impacts the firm’s profitability.
What does a high DOL indicate?
Unfortunately, the excessive use of financial leverage by many companies in these sectors has played a paramount role in forcing a lot of them to file for Chapter 11 bankruptcy. If the operating leverage explains business risk, then FL explains financial risk. However, operating leverage directly influences the sales level and is called first-order leverage, whereas FL indirectly influences sales and is called second-order leverage. If the financial leverage is positive, the finance manager can try to increase the debt to enhance benefits to shareholders.
Degree of operating leverage formula
Some companies earn less profit on each sale but can have a lower sales volume and still generate enough to cover fixed costs. In the base case, the ratio between the fixed costs and the variable costs is 4.0x ($100mm ÷ $25mm), while the DOL is 1.8x – which we calculated by dividing the contribution margin by the operating margin. The degree of combined leverage measures the cumulative effect of operating leverage and financial leverage on the earnings per share. To calculate the degree of operating leverage, you will need to know the company’s sales, variable costs, and operating income. While this is riskier, it does mean that every sale made after the break-even point will generate a higher contribution to profit. There are fewer variable costs in a cost structure with a high degree of operating leverage, and variable costs always cut into added productivity—though they also reduce losses from lack of sales.

How are the concepts of financial leverage and Operating Leverage related?
The average tax applicable to the company is 30% and corporate dividend tax is 20%. DOL is based on historical data and may not accurately predict future performance. Additionally, it does not consider the impact of external factors like market conditions and economic changes. Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing.
- It measures a company’s sensitivity to sales changes of operating income.
- Where earnings are either equal to fixed financial charge or unfavorable, debt financing should not be encouraged.
- The degree of operating leverage shows the change in operating income to the change in the revenues or sales of a company.
How Does Cyclicality Impact Operating Leverage?
As can be seen from the example, the company’s degree of operating leverage is 1.0x for both years. Looking back at a company’s income statements, investors can calculate changes in operating profit and sales. Investors can use the change in EBIT divided by the change in sales revenue to estimate what the value of DOL might be for different levels of sales.
Therefore, poor managerial decisions can affect a firm’s operating level by leading to lower sales revenues. This is actually caused by the “amplifying effect” of using fixed costs. Even if sales increase, fixed costs do how is computer software classified as an asset not change, hence causing a larger change in operating income. If sales revenues decrease, operating income will decrease at a much larger rate. It measures a company’s sensitivity to sales changes of operating income.
With each dollar in sales earned beyond the break-even point, the company makes a profit. Conversely, retail stores tend to have low fixed costs and large variable costs, especially for merchandise. Because retailers sell a large volume of items and pay upfront for each unit sold, COGS increases as sales increase.


